- Welcome my DevOps blog./
- 🔰Posts/
- 🗂️My Trainings/
- AWS Trainings and Certifications/
- 🏅AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner/
- AWS Global Infrastructure/
AWS Global Infrastructure
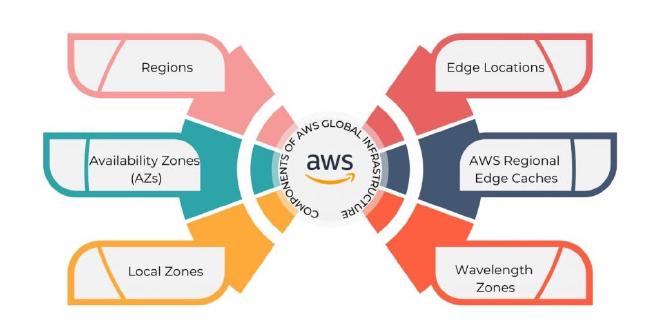
Table of Contents
A Global Application is an application deployed in multiple geographies. On AWS this could be Regions and / or Edge Locations.
- Decreased Latency
- Disaster Recovery
- (DOS / DDoS) Attack protection (distributed global infrastructure is harder to attack)
More: https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/global-infrastructure/
AWS Global Infrastructure Overview - Regions, Availability Zones, Edge Locations and more
Route53 #
Route53 is managed DNS.

Route53 Routing Policies #
- Simple Routing Policy - No health checks, just DNS check
- Weighted Routing Policy - Specify what amount of traffic goes where (i.e. 70% = Server1, 20% = Server2, 10% = Server3. Simple form of Load Balancing)
- Latency Routing Policy - Based on latency - minimizing the latency between user and the server sending the traffic that is geographically (latency-based) closer to the user
- Failover Routing Policy - Disaster Recovery (DR) - based on Health Checks
- Geolocation Routing Policy - Routing based specifically on Geolocation
- IP-based Routing Policy - Route the traffic based on the IP address originates from
More on Routing Policies: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/Route53/latest/DeveloperGuide/routing-policy.html
AWS Route 53 Course
Registering a domain #
# Register a Domain
Route 53 > Registered Domains > Register Domain > CHOOSEADOMAIN.COM
# Hosted zones
Route 53 > Hosted zones > select "CHOOSEADOMAIN.COM" > Update the DNS records with the right EC2 instances, select an adequate Routing Policy
More about Registering and managing domains: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/Route53/latest/DeveloperGuide/registrar.html
More about Route 53: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/route53/
Amazon CloudFront #
- Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Improves read performance, content cached at the edge
- Improves users experience
- Many Points of Presence globally (Edge Locations, Edge Caches)
- DDoS protection (because it’s distributed globally)
- Integrated with Shield and AWS WAF (Web Application Firewall)
CloudFront - Origins #
- S3 Bucket
- For distributing files and caching them at the edge
- For uploading files to S3 through CloudFront
- Secured using Origin Access Control (OAC)
- VPC Origin
- For applications hosted in VPC private subnets
- Application Load Balancer / Network Load Balancer / EC2 Instances
- Custom Origin (HTTP)
- S3 website (must first enable the bucket as a static S3 website)
- Any public HTTP backend

CloudFront vs S3 Cross Region Replication #
CloudFront #
- Global Edge Network
- Files are cached for a TTL (day?)
- Use case: static content that must be available everywhere
S3 Cross Region Replication #
- Must be setup for each region you want your replication to happen
- Files are updated in near real-time
- Read-only
- Use case: dynamic content that needs to be available at low-latency in few regions only
S3 Transfer Acceleration #
Increase transfer speed by transferring files to an AWS edge location which will forward the data to the S3 bucket in the target region.
AWS Global Accelerator #
AWS Global Accelerator is used to improve global application availability and performance using the AWS global network.
Leverage the AWS internal network to optimize the route to your application (60% improvement).

More about AWS Global Accelerator:
- https://aws.amazon.com/global-accelerator/
- https://docs.aws.amazon.com/global-accelerator/latest/dg/what-is-global-accelerator.html
- https://speedtest.globalaccelerator.aws
AWS Global Accelerator vs CloudFront #
- They both use AWS global network and it’s edge locations
- Both services integrate with AWS Shield for DDoS protection
- CloudFront - Content Delivery Network
- Improves performance for cacheable content (images, videos, etc.)
- Content is served at the edge
- Global Accelerator
- No caching, proxying packets at the edge to applications running in one or more AWS regions
- Improves performance for a wide range of applications running in one or more AWS regions
- Improves performance for a wide range of applications over TCP or UDP
- Good for HTTP use cases that require static IP addresses
- Good for HTTP use cases that require deterministic, fast, regional failover
AWS Outposts #
AWS Outposts = Hybrid Cloud appliances. #
Outposts are “server racks” that offer the same AWS infrastructure, services, API’s & tools to build your own applications on-premises just as in the cloud.
AWS will setup and manage Outposts racks within your on-premises infrastructure. #
Benefits
- Low latency access to on-premises system
- Local data processing
- Data residency
- Easier migration from on-premises to the cloud
- Fully managed service
- Some example services that work on Outposts:
Wavelength #
Wavelength Zones are infrastructure deployments embedded within the telecommunication providers datacenters at the edge of the 5G networks.
- Ultra low latency applications through 5G networks
- Traffic doesn’t leave the Communication Service Provider’s (CSP) network
- High bandwidth and secure connection to the parent AWS Region
- No additional charges or service agreements
- Use cases:
- Smart Cities
- ML-assisted (Machine Learning) diagnostics
- Connected Vehicles
- Interactive Live Video Streams
- AR / VR
- Real-time gaming
AWS Local Zones #
AWS Local Zones allow placing compute, storage, database and other selected AWS services closer to the users to run latency-sensitive applications.
It is an “Extension of AWS Region”.
Example: #
- AWS Region: N. Virginia (us-east-1)
- AWS Local Zones: Boston, Chicago, Dallas, Houston, Miami, …
Compatible with: #
More about AWS Local Zones: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/local-zones/latest/ug/what-is-aws-local-zones.html
Summary #
Route 53 - Global DNS
- Great to route users to the closest deployment with least latency
- Great for Disaster Recovery - DR - Strategies
CloudFront - Global CDN - Content Delivery Network
- Replicate part of your application to AWS Edge Locations - decreased latency
- Cache common requests - improved user experience and decreased latency
S3 Transfer Acceleration
- Accelerate global uploads & downloads into Amazon S3
AWS Global Accelerator
- Improve global application availability and performance using the AWS global network
AWS Outposts
- Deploy Outposts racks in an on-premises datacenter to extend some AWS services and for easier migration
AWS Wavelength
- Brings AWS services to the edge of the 5G networks
- Ultra-low latency applications
AWS Local Zones
- Bring AWS resources (compute, database, storage, …) closer to your users
- Good for latency-sensitive applications
» Sources « #
Global Infrastructure: https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/global-infrastructure/
Route 53 #
Route 53: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/route53/ Route 53 Routing Policies: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/Route53/latest/DeveloperGuide/routing-policy.html Registering and managing domains: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/Route53/latest/DeveloperGuide/registrar.html
CloudFront #
CloudFront: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cloudfront/
AWS Global Accelerator #
https://aws.amazon.com/global-accelerator/ https://docs.aws.amazon.com/global-accelerator/latest/dg/what-is-global-accelerator.html https://speedtest.globalaccelerator.aws
AWS Local Zones #
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/local-zones/latest/ug/what-is-aws-local-zones.html
» References « #
» Disclaimer « #
This series draws heavily from Stephane Maarek’s Ultimate AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner course on Udemy.
His content was instrumental in helping me pass the certification.
| About the instructor | |
|---|---|
| 🌐 Website | 📺 YouTube |
| 𝕏 x.com |

